There are many sexually transmitted diseases and infections. You may have heard about infections like HIV, gonorrhea, or even chlamydia. One STDI that you may not have heard of or perhaps not have heard as much about is called Trichomoniasis. Read on to find out more about Trichomoniasis symptoms, treatment, and prevention of this surprisingly common STI.
What is Trichomoniasis?
Trichomoniasis is a sexually transmitted infection that is caused by a parasite. Many people refer to this particular infection as “trich” for short, since the full word can be difficult to pronounce correctly. Out of all of the sexually transmitted infections, Trichomoniasis happens to be the most common. The good news is that it is a curable infection. The infection is most common among sexually active women in their twenties. The infection is only transmitted through sexual contact, most commonly from vaginal intercourse between a man and a woman or sexual activity between two women involving the vulva.
The infection is caused by a parasite called Trichomonas vaginalis, which is a flagellated motile protozoan. It infects over 170 million people globally. In the United States alone, it is estimated that nearly 4 million people have the infection. However, over 70% of infected persons will experience no symptoms associated with the infection. These people are classified as being asymptomatic. The Trichomonas parasite is not visible to the eye and so it must be viewed with a microscope. The parasites will typically reproduce every seven to twelve hours on average.
Disclaimer: condom-sizes.org is supported by its readers. When you buy through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission. Learn more.
Click here to order a Comprehensive Home STD Test Pack!
Symptoms of Trichomoniasis
Trichomoniasis symptoms often never appear in infected persons. However, it is important to note that when they do appear, the symptoms of Trichomoniasis are different for men and women. Women may experience vaginal itching and pain with urination. They may also experience vaginal discharge which may be yellow, gray, green, frothy, and foamy or have a foul odor. For men, symptoms might include discharge from the urethra, pain during urination, and swelling or pain in the scrotum.
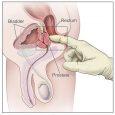
The diagnosis of Trichomoniasis is made by taking a sample of the urethral or vaginal discharge that occurs and viewing it under a microscope. For women, the specimen can be taken during a pelvic exam, in which the doctor inserts a cotton-tipped applicator into the vagina to retrieve a discharge sample. Trichomoniasis parasites are not usually visible using urine-based tests.
The parasites, which can be up to 15 mm long, will only be visible under a microscope. The Trichomoniasis parasites are typically shaped like a pear and have tails at one end. Some specimen samples may also need to be sent to a laboratory in order to confirm the presence of Trichomoniasis. When a diagnosis of Trichomoniasis is made, a doctor will often order a panel of tests for other sexually transmitted diseases.
Treatment for Trichomoniasis
Trichomoniasis is most often treated with antibiotics. Typically, tinidazole (Tindamax) or metronidazole (Flagyl) are the drugs of choice to effectively kill this particular parasite. These drugs are most often given in one very large dose. While there are creams and gels available for treatment, oral medications have been found to be the most effective method for curing the infection. During treatment, it is critical that both sexual partners refrain from having unprotected sex.
The antibiotics will typically take about one week to cure the infection. Since the antibiotics used to kill these parasites are very strong, they can sometimes have side effects which can include headaches, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, or a metallic taste in the mouth. It is also important to avoid drinking alcohol within twenty-four to seventy-two hours after taking the antibiotics you are prescribed, as mixing them with alcohol can cause severe side effects including nausea and vomiting.
If Trichomoniasis is left untreated, inflammation and damage can occur which causes a woman to have a higher risk of being infected by HIV and a higher risk of transmitting HIV to a partner. In pregnant women, Trichomoniasis can cause premature births or early delivery due to the infection causing internal membranes to rupture.
Prevention of Trichomoniasis
As with other sexually transmitted infections, the absolute best way not to get infected is to practice abstinence. The next best method to protect you is to use a condom, correctly and consistently.
Sex with partners with which you know their sexual history and any infections they might have is also helpful. Try to avoid having sex with multiple partners or anyone who you do not know well. If you think you may be infected with any sexually transmitted disease, be sure to see a doctor as soon as possible. Most sexually transmitted diseases are either curable or treatable.
Whenever you experience any type of unusual discharge, pain, itching, or swelling in your genital area, it is always a good idea to seek the advice of a doctor and to get tested. So if you think you may have been exposed to any sexually transmitted diseases, be sure to get tested as soon as possible.
Remember that many sexually transmitted diseases show no symptoms, especially in the early stages. You could have an infection and not be aware of it, therefore any sexual contact you have may be putting your partner(s) at risk of infection.